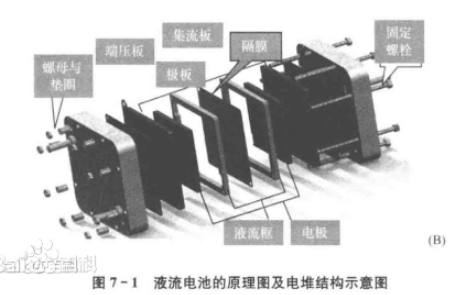
Figure 1 shows the schematic diagram and stack structure of a flow battery. The positive and negative electrolytes of the battery are stored in two separate tanks, and the electrolyte is circulated through the battery using a liquid pump. Inside the fuel cell stack, the positive and negative electrolytes are separated by ion exchange membranes (or ion separators), and the battery is connected to an external load and power source. Flow battery technology, as a new type of large-scale and efficient electrochemical energy storage (electricity) technology, achieves the conversion and energy storage of electrical and chemical energy through the valence state changes of reactive active substances. In a flow battery, the active substance is stored in the electrolyte and has fluidity, which enables the separation of the electrochemical reaction site (electrode) and the energy storage active substance in space. The battery power and capacity design are relatively independent, making it suitable for large-scale energy storage needs. Unlike ordinary secondary batteries, the energy storage active material of flow batteries is completely separated from the electrodes, and the power and capacity designs are independent of each other, making it easy to combine modules and place battery structures; Electrolyte stored in storage tanks will not undergo self discharge; The fuel cell stack only provides a place for electrochemical reactions and does not undergo redox reactions on its own; The active substance dissolves in the electrolyte, greatly reducing the risk of electrode dendrite growth piercing the separator in flow batteries; At the same time, the flowing electrolyte can take away the heat generated during the battery charging/discharging process, avoiding structural damage or even combustion caused by battery heating.